RBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2025-26 Released: Download Latest and Revised RBSE Class 12th Syllabus PDF with Subject-wise
Table of Contents
The Rajasthan Board of Secondary Education has released the RBSE 12th syllabus 2025-26 on its official website @rajeduboard.rajasthan.gov.in. The syllabus is available in subject-wise format. This article also has direct links for subject-wise RBSE 12th syllabus PDF.
The board releases syllabi for all streams - science, commerce, and arts. The Rajasthan class 12 syllabus includes topics for both theory and practical exams. Students need to go through the detailed syllabus before starting their preparation for RBSE 12th exam 2026.
The board has also removed some topics from the class 12 RBSE syllabus to ease the difficulty level. Students must keep these PDFs handy to score higher marks in the final examination. This article covers more information on how to download these PDFs, important topics in the RBSE 12th syllabus 2025-26, and more.
RBSE 12th Syllabus 2025-26 PDF Download
Students can download the RBSE 12th syllabus 2026 from the board's official website @rajeduboard.rajasthan.gov.in. Along with the syllabus, candidates should also be aware of RBSE 12th exam pattern to score well in the exam.
Tabulated below is the direct link to the PDF for RBSE syllabus for 12th.
| Content | PDF Link |
| RBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2026 | Click Here |
RBSE 12th Syllabus 2025-26 - Science Stream
The subjects covered in the RBSE syllabus 2026 class 12 science are mathematics, biology, physics, chemistry, geology, and more. The updated syllabus of class 12 RBSE 2026 includes a chapter-wise marking scheme for theoretical exams, practical exams, and internal assessments.
Candidates can review the RBSE 12th science syllabus 2026 below and study accordingly.
RBSE 12th Syllabus for Physics
The unit-wise topics and chapters per the RBSE class 12 physics syllabus 2026 are tabulated below. The exam for physics class 12th contains 56 marks for theory, 30 for practical, and 14 for internal assessment.
| Units | Chapter | Topics | Marks Allotment |
| 1 & 2 | Electrostatics | Electric Charges and Fields | 4 |
| Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance | 3 | ||
| Current electricity | 4 | ||
| 3 | Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism | Moving Charges And Magnetism | 4 |
| Magnetism And Matter | 3 | ||
| 4 | Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents | Electromagnetic Induction | 4 |
| Alternating Current | 5 | ||
| 5 | Electromagnetic Waves | 2 | |
| 6 | Optics | Ray Optics And Optical Instruments | 7 |
| Wave Optics | 5 | ||
| 7 | Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter | 4 | |
| 8 | Atoms and Nuclei | Atmos | 4 |
| Nuclei | 3 | ||
| 9 | Electronic Devices | Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices, And Simple Circuits | 4 |
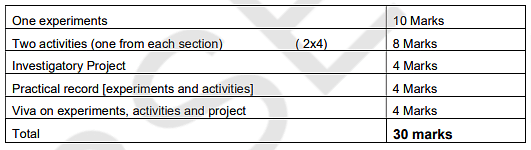
The RBSE class 12 physics syllabus 2026 for the practical exam is given below.
RBSE 12th Syllabus for Chemistry
The theory portion contains 56 marks, the practical exam consists of 30 marks, and the rest of the 14 marks are assigned in the internal assessment.
The unit-wise topics and chapters as per the RBSE class 12 physics syllabus 2026 are tabulated below. The detailed marking scheme for the RBSE 12th chemistry exam is also mentioned below.
| Units | Marks Allotment |
| Solutions | 6 |
| Electro Chemistry | 6 |
| Chemical Kinetics | 6 |
| d and f- block elements | 5 |
| Coordination Compounds | 5 |
| Haloalkanes and Haloarenes | 6 |
| Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers | 6 |
| Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids | 7 |
| Amines | 5 |
| Biomolecules | 4 |
| Total | 56 |
The class 12 RBSE Chemistry syllabus 2026 for the practical exam is given below.

RBSE 12th Syllabus for Biology
The RBSE class 12 biology syllabus 2026 is provided in the table below with the chapter-wise marking scheme. The Biology exam contains 56 marks for theory, 30 marks for practical, and 14 marks for internal evaluation.
| Chapters | Marks Allotment |
| Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants | 5 |
| Human Reproduction | 4 |
| Reproductive Health | 2 |
| Principles of Inheritance and Variation | 5 |
| Molecular Basis Of Inheritance | 6 |
| Evolution | 3 |
| Human Health and Disease | 6 |
| Microbes in Human Welfare | 5 |
| Biotechnology: Principles and Processes | 4 |
| Biotechnology and its Applications | 4 |
| Organisms and Population | 4 |
| Ecosystem | 5 |
| Biodiversity and Conservation | 3 |
| Total | 56 |
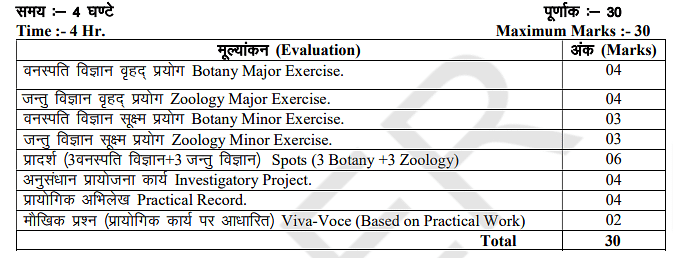
The RBSE 12th Biology syllabus 2026 for the practical exam is illustrated below.
RBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus 2026
Mathematics contains 100 marks that are further divided into 80 marks for theory papers and 20 marks for Practical/Viva. The marking scheme for the RBSE 12th syllabus 2026 for Maths is tabulated below for the student's reference.
| Units | Marks Allotment |
| Relations and Functions | 7 |
| Algebra | 10 |
| Calculus | 36 |
| Vectors and Three-Dimensional Geometry | 16 |
| Linear Programming | 4 |
| Probability | 7 |
RBSE 12th Syllabus 2025-26 - Commerce Stream
The RBSE 12th commerce syllabus 2026 consists of major subjects such as accountancy, business studies, economics, statistics, mathematics, etc. Thus, students should go through the given syllabus and prepare.
RBSE 12th Syllabus for Accountancy
Refer to the table below to learn more about the RBSE 12th syllabus 2026 for accountancy subject.
Part A
I. Introduction to Partnership
- Meaning, Definition, Need Features, and Types of Partnership
- Partnership Deed- Meaning contents, Rules in the absence of Partnership Deed
- Partners Capital Accounts Fixed and Fluctuating
- Distribution of Profit among partners- Profit and Loss
- Appropriation Account
- Interest on Partners Capital and Interest on Drawings
- Past Adjustments/Adjustments in Closing Accounts
- Guarantee of Minimum Profit to a Partner
II. Admission of New Partner
- Rights of a New Partner
- New Profit Sharing Ratio
- Sacrificing Ratio
- Goodwill- Meaning, Methods of Valuation, and Accounting Treatment of Goodwill
- Revaluation of Assets and Liabilities
- Revaluation Accounts and Memorandum Revaluation Account
- Distribution of Accumulated Profit, Loss or Reserve
- Adjustment of Partners Capital
- Accounting Treatment of Change in Profit Sharing Ratio among Existing Partners
III. Accounting for Retirement and Death of Partner
- Meaning and Methods of Retirement of a Partner
- New Profit Sharing Ratio and Gain Ratio
- Accounting Treatment of Goodwill on retirement or death of a partner
- Accounting Treatment for revaluation of Assets and reassessment of Liabilities
- Accounting Treatment of Accumulated Profit/Loss, Reserve on Retirement or Death
- Computation and Payment of amount Due to retiring or deceased partner
IV. Company Accounts: Issue of Shares and Debentures
- Company: Meaning and Characteristics, kinds and classification
- Shares and Kinds of Shares
- Accounting Treatment of Issue of Shares at Par and at Premium
- Accounting Treatment of Issue of Shares for Cash and for
- Consideration other than Cash
- Under Subscription and Over Subscription of Shares
- Sweat Equity Shares, Right Shares, Employee Stock Option Plan, and Escrow Account
- Meaning, Characteristics, and Types of Debentures
- Accounting Treatment of Issue of Debentures
- Accounting Treatment of Issue of Debentures for Consideration other than cash
- Disclosure of Debentures in Balance Sheet
- Accounting Treatment of Interest on Debentures
- Writing off Discount or Loss on Issue of Debentures
V. Joint Venture Accounts
- Meaning and Introduction of Joint Venture
- Methods of Accounting for Joint Venture
- Separate Books are Kept
- No Separate Books are Kept
VI. Accounting for Non-Trading Organisations and Professional Persons
- Meaning of Non-Trading organization and Books Kept by them
- Preparation of Receipt and Payment Account
- Preparation of Income and Expenditure Account
- Preparation of Balance Sheet
- Preparation of Opening and Closing Balance Sheet from Receipt and Payment Accounts and Income and Expenditure Accounts
- Difference Between Receipt and Payment Account and Income and
- Expenditure Account
Part B
I. Application of Electronic Spreadsheet in Accounting
- Meaning, Definition, Objectives, Nature, and Characteristics of Financial Statements
- Objects, Merits, Limitations, and Process of Financial Analysis
- Techniques of Financial Statement Analysis
- Comparative Financial Statement
- Common Size Financial Statement
II. Ratio Analysis
- Meaning of Ration Analysis
- Meaning of Ratio and its Expression
- Objectives and Limitations of Ration Analysis
- Precaution in Using Ratios
- Classification of Ratios:
- Liquidity Ratios
- Solvency Ratios
- Activity Ratios
- Profitability Ratios
- Investment Analysis Ratios
Part C
I. Application of Electronic Spreadsheet in Accounting
- Utility of Spread Sheet
- Features of Microsoft Excel
- Spread Sheet sources and Use them in Accounting
- Financial Analysis through Spreadsheets
- Elements of Excel Spread Sheet
- Difference between Spread Sheet and Workbook
II. Computerized Accounting System
- Computerized Accounting System: Meaning, components, capabilities, Utility, benefits
- Automation of the Accounting Process
- Composition of Computerized Accounting System
- Management Information System and Accounting
- Information System
- Computerized Accounting Software
- Manual and Computerized Accounting system
Refer to the image mentioned below to get detailed information on the RBSE 12th Accountancy paper for the academic year 2026.


RBSE 12th Syllabus for Business Studies
As per the business studies class 12 RBSE syllabus, the subject consists of 8 units. The units and topics-wise details are tabulated below.
I. Management
- Meaning, Definition, Nature
- Functional Areas, Process Principles, Managerial Roles
- Emerging Trends: MBO, MBE Strategic Management Stress Management
II. Motivation and Leadership
- Meaning, Definition, Needs Techniques Theories-Maslow
- Herzberg, Leadership-Meaning Definition, Traits, Styles
III. Advertisement
- Meaning, Definition, Objectives, Means, Merit, Demerits, Importance,
- Marketing Management Meaning, Definition, Process, Importance Sales
- Promotion - Introduction, Importance, Types, and Methods
IV. Entrepreneurship
- Introduction, Nature Importance, Barriers, Entrepreneur Trades, Types, Women’s Rural Entrepreneur, EDP- Government Efforts
V. Insurance
- Introduction, Scope, Types, Objective, Functions, Needs
- Importance, Social Security, Insurance Agents Functions
VI. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
- Introduction, Legal Provision, Importance
The detailed marking scheme of the Business Studies for class 12 is mentioned below.
| Units | Marks |
| Nature and Significance of Management | 6 |
| Principles of Management | 7 |
| Business Environment | 3 |
| Planning | 6 |
| Organising | 8 |
| Staffing | 7 |
| Directing | 8 |
| Controlling | 5 |
| Financial Management | - |
| Marketing | - |
| Consumer Protection | - |
RBSE 12th Syllabus for Economics
Mentioned below are the details regarding the RBSE 12th syllabus 2026 for economics. It consists of two sections - microeconomics and macroeconomics.
| Units | Marks |
| Part A: Introductory Microeconomics- Introduction National Income Accounting |
8 |
| Money and Banking | 8 |
| Income and Employment | 8 |
| Government Budget | 8 |
| Open Economy | 8 |
| Part B: Introductory Microeconomics- Introduction | 6 |
| Consumer Behaviour | 10 |
| Concept of Production and Costs | 10 |
| Perfect Competition Market Equilibrium |
8 |
| Non-Competitive Markets | 6 |
| Total | 80 |
RBSE 12th Syllabus 2025-26 - Arts/Humanities Stream
The class 12 arts syllabus 2026 RBSE consists of subjects like geography, history, political science, economics, etc. Thus, candidates need to go through the following subjects and prepare.
RBSE 12th History Syllabus
The RBSE class 12th syllabus 2026 for history is tabulated below with units and a chapter-wise marking scheme.
The History exam contains 80 marks for the theory exam including 5 marks for map work and 20 marks for internal evaluation. As per the class 12 RBSE syllabus 2026, students can refer to the NCERT textbook to know the syllabus of map work.
| Units | Chapters | Marks Allotment |
| Themes in Indian History, Part I | The Harappan Civilisation - Bricks, Beads and Bones | 6 |
| Early States and Economies - Kings, Farmers and Towns | 6 | |
| Early Societies - Kinship, Caste, and Class (C. 600 BCE-600 CE) | 6 | |
| Thinkers, Beliefs, and Buildings - Cultural Developments | 7 | |
| Themes in Indian History, Part II | Through the Eyes of Travellers, Perceptions of Society | 6 |
| Sufi Traditions, Changes in Religious Beliefs and Devotional Texts (C. Eighth to Eighteenth Century) | 7 | |
| An Imperial Capital: Vijayanagara (c. Fourteenth to Sixteenth Century) | 6 | |
| Peasants, Zamindars and the State-Agrarian Society and the Mughal Empire (c. Sixteenth- Seventeenth Centuries) | 6 | |
| Themes in Indian History, Part III | Colonialism and the Countryside-Exploring Official Archives | 6 |
| Rebels and the Raj- The Revolt of 1857 and Its Representations | 6 | |
| Mahatma Gandhi and the Nationalist Movement: Civil Disobedience and Beyond | 7 | |
| Framing the Constitution - The Beginning of a New Era | 6 | |
| Map Work | 5 |
RBSE 12th Geography Syllabus
- Human Geography-definition, nature, subject matter, and significance.
- Major tribes in the world - Eskimos, Bushman, Gond, Bhil: their distribution, economic and cultural characteristics.
II. World Population
- World population - distribution, factor affecting population density.
- Population growth - causes, problems and solutions, demographic transition theory.
- Population structure - age group, sex ratio, rural-urban.
- Migration - concept, types, aspects, and problems.
- Concepts of human development.
III. Human Settlements in the World
- Settlement - types of rural and urban settlements, patterns, and problems.
- Urban slum - problems and solutions.
- A case study of the Dharavi slum area in Mumbai.
IV. Human Occupations
- Primary occupations - introduction, agriculture, mining, hunting, animal husbandry, fishing, and ancestral gathering.
- Secondary occupations - types of industries, determination of industrial location, agro-based industries, manufacturing industries.
- Tertiary, quaternary, and quandary occupations.
V. World: Transport, Network, and Trade
- Surface transport - principal international roads and railways.
- Water transport - principal inland and oceanic waterways, ports, Suez and Panama Canal sea routes.
- Air transport - principal air routes and airports.
- Pipeline transport - principal oil and gas lines.
- International trade and role of India.
- Modern means of mass communication - satellite, internet, mobile, etc.
VI. Environment
- Environmental problems - pollution, acid rain, greenhouse effect, ozone layer depletion.
- World environmental summits.
VII. Map Work
Map work based on the subject matter mentioned above on the outline map of the world.
Part B - India: Population and Economics
VIII. India - Population
- Distribution, density, population, growth, and aspects.
- Population structure - age group, literacy, sex ratio, literacy, rural and urban.
- Racial groups, religious composition, and foreign impact on Indian culture.
IX. Resources
- Resources - classification, conservation, and sustainable development.
- Non-biotic resources - land, water, minerals (iron, copper, aluminum, mica).
- Biotic resources - animal wealth, forest, and fisheries.
- Energy resources - conventional (coal, petroleum, hydroelectricity) and nonconventional (nuclear, organic, wind, and solar).
X. Agriculture
- Types of agriculture - subsistence and commercial, wet farming and dry farming, intensive and dispersed, organic and chemical fertilizes based horticulture.
- Major crops - distribution and production of wheat, rice, cotton, sugarcane, and tea.
XI - Manufacturing Industries and Transport
- Industrial development in India, major industries - iron steel, aluminum, cement, cotton textile, sugar, and engineering.
- Transport - land, water, air, oil, and gas pipelines
XII. Development and Planning
- Development and planning - major plans and implementation.
- Regional planning - regional imbalances, desert development program, tribal area development program, mountain area development.
- Poverty alleviation and employment programs, MGNREGA - role and impact.
- Sustainable development - traditional and modern viewpoints.
XIII. Rajasthan - Population and Economy
- Rural development - dairy and cottage industries.
- Major industries - cotton textile, cement.
- Minerals - marble, copper, zinc, silver, tungsten, gypsum, and petroleum.
- (4) Major irrigation projects - Chambal, Indira Gandhi and Mahi.
- (5) Problem of drinking water and plans.
- (6) Population distribution, density, sex ratio, and literacy.
- (7) Major tribes - Meena, Bhil, Garasia, Saharia and Damor.
XIV. Map Work
Map Work based on the subject matter of part (B) above on the outline maps of India and Rajasthan
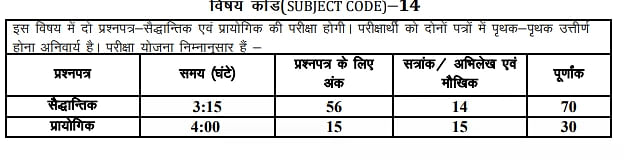
The RBSE 12th Geography syllabus 2026 for the practical exam is illustrated below.

RBSE 12th Syllabus for Political Science
Political science is an important subject in the arts stream. The different parts of the political science class 12 syllabus 2026 RBSE are mentioned below along with the marking assignment.
| Parts | Marks Allotment |
| Contemporary World-Politics | 40 |
| Politics of India Since Independence | 40 |
| Total | 80 |
RBSE Class 12 Language Subject Syllabus 2026
The RBSE class 12 syllabus 2026 consists of chapters and topics to be covered in the board exam for language-based subjects such as English, Hindi, Sanskrit, and others. The exams for language-based subjects contain 80 marks.
The RBSE class 12th syllabus 2026 for language-based subjects is provided in the following section.
RBSE 12th English Syllabus
The table below includes the RBSE class 12 English syllabus 2026 which students can refer to.
| Sections | Marks Allotment |
| Reading | 15 |
| Writing | 15 |
| Grammar | 8 |
| Text Book- Rainbow | 28 |
| Supp. Book- Panorama | 14 |
Also Read: RBSE 12th Sample Paper 2026
How to Download RBSE 12th 2026 Syllabus?
Students preparing for the RBSE 12th exam must go through the entire syllabus carefully and schedule their timetable accordingly. Moreover, the detailed steps to download the RBSE 12th syllabus 2026 are given below.
- Step 1: Candidates need to visit the official website of the board - rajeduboard.rajasthan.gov.in.
- Step 2: Candidates can then navigate to the home page and click on the 'अनुदेशिका 2020 एवं पाठयक्रम 2026’ in the left-hand panel.
- Step 3: The 'RBSE Syllabus 2026 Class 12' link will be displayed on the screen.
- Step 4: Candidates need to click on the 'Course 2026 for Class 12' link and the PDF file for all the subjects will be displayed on the screen.
- Step 5: At the final step, candidates can download the syllabus and start preparing for the board examination.
FAQs on RBSE 12th Syllabus
Q: From where can the students download the RBSE class 12 syllabus 2026?
Q: What is the medium of RBSE 12th syllabus 2026?
Q: Is the RBSE 12th 2026 syllabus available for all subjects?
Q: What is the blueprint for RBSE class 12 2026?
Q: Is the syllabus reduced for RBSE class 12?

![Maharshi Dayanand Saraswati University, [MDSU] Ajmer](https://media.getmyuni.com/azure/college-image/small/maharshi-dayanand-saraswati-university-mdsu-ajmer.webp)





![Ajmer Institute of Technology, [AIT] Ajmer](https://media.getmyuni.com/azure/college-image/small/ajmer-institute-of-technology-ait-ajmer.jpg)

![Aryabhatta College of Engineering and Research Centre, [ACERC] Ajmer](https://media.getmyuni.com/azure/college-image/small/aryabhatta-college-of-engineering-and-research-centre-acerc-ajmer.jpg)