Table of Contents
AP EAMCET Chemistry syllabus 2025 contains topics like General Principles of Metallurgy, Group-16 Elements, Coordination Compounds, etc. The official AP EAMCET website also provides a detailed syllabus for Chemistry. Majority of the Chemistry AP EAMCET weightage 2025 can be covered with Class 11 and Class 12 NCERT books.
Candidates are advised to focus on high-weight topics in the Chemistry weightage for AP EAMCET 2025. A total of 40 questions are asked in the Chemistry section of the AP EAMCET exam.
Download: AP EAMCET Previous Years Question Papers
AP EAMCET Chemistry Syllabus 2025
The AP EAMCET Chemistry syllabus 2025 can be reviewed on the official website at cets.apsche.ap.gov.in. The detailed topics and pattern of the AP EAMCET exam are also available. Students must check the in-depth syllabus to identify topics they may need a stronghold on and work on them.
Students can expect the difficulty level for AP EAMCET syllabus 2025 topics for Chemistry to be moderate. The Chemistry syllabus for AP EAMCET can be revised by solving the AP EAMCET mock tests and the previous year's question papers.
Also Read: AP EAMCET Physics Syllabus 2025
AP EAMCET Chemistry Syllabus PDF Download 2025
The syllabus for Organic Chemistry for AP EAMCET 2025 and Inorganic Chemistry is available in the PDF link below. The syllabus PDF can be downloaded for free for reference. Students can review the Chemistry syllabus PDF by clicking on the link.
The PDF sets can be downloaded by clicking on the "Download" button on the syllabus PDF.
| AP EAMCET Syllabus 2025 for Chemistry | Download PDF |
Also Read: AP EAMCET Chapter Wise Weightage 2025
AP EAMCET Chemistry Syllabus 2025 Topics
The detailed sub-topics within the AP EAMCET Chemistry syllabus 2025 must be marked for preparation. Students can review the in-depth AP EAMCET syllabus 2025 for Chemistry from the following section. Candidates may refer to this page for any changes in the official syllabus.
AP EAMCET 2025 Chemistry Syllabus in Detail
The AP EAMCET 2025 Chemistry syllabus comprises Group 16 Elements, Group 17 Elements, Coordination Compounds, Biomolecules, Hydrocarbons, etc. A detailed view of the AP EAMCET 2025 Chemistry syllabus is essential to understand the basic concepts. The AP EAMCET syllabus 2025 for Chemistry can be reviewed here:
Atomic Structures:
- Stability of Half-Filled and Completely Filled Orbitals. Developments to the Bohr’s Model of Atom.
- Particle Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation.
- Wave Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation.
- Developments to the Bohr’s Model of Atom.
- Wave Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation. Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle. Quantum Mechanical Model of an Atom. Bohr’s Model for Hydrogen Atom. Explanation of Line Spectrum of Hydrogen.
- Dual Behaviour of Matter. Quantum Mechanical Model of an Atom. Important Features of Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom. Orbitals and Quantum Numbers.
- Aufbau Principle, Electronic Configurations of Atoms. Particle Nature of Electromagnetic Radiation- Planck’s Quantum Theory. Pauli’s Exclusion Principle and Hund’s Rule of Maximum Multiplicity.
- Bohr’s Model for Hydrogen Atom. Limitations of Bohr’s Model. Quantum Mechanical Considerations of Sub-Atomic Particles. Dual Behaviour of Matter.
- Limitations of Bohr’s Model. Quantum Mechanical Considerations of Sub-Atomic Particles. Important Features of Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom.
- Orbitals and Quantum Numbers. Filling of Orbitals in Atoms. Shapes of Atomic Orbitals. Energies of Orbitals. Filling of Orbitals in Atoms.
- Electronic Configurations of Atoms. Stability of Half-Filled and Completely Filled Orbitals.
Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties:
- Nomenclature of Elements With Atomic Number Greater Than 100.
- Electronic Configuration of Elements and the Periodic Table. Periodic Trends and Chemical Reactivity.
- Electronic Configuration and Types of Elements S,P,D. And F Blocks.
- Trends in Physical Properties: (A) Atomic Radius, (B) Ionic Radius (C) Variation of Size in Inner Transition Elements, (D) Ionization Enthalpy,(E) Electron Gain Enthalpy, (F) Electro Negativity. Periodic Modern Periodic Law and Present Form of the Periodic Table.
- Trends in Chemical Properties: (a) Valence or Oxidation States, (B) Anomalous Properties of Second Period Elements - Diagonal Relationship.
Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure:
- Valence Bond Theory-Orbital Overlap Concept. Directional Properties of Bonds.
- Overlapping of Atomic Orbitals. Types of Overlapping and Nature of Covalent Bonds. Strength of Sigma and Pi Bonds-Factors Favouring the Formation of Covalent Bonds. Ionic or Electrovalent Bond.
- Factors Favourable for the Formation of Ionic Compounds- Crystal Structure of Sodium Chloride.
- Bond Parameters - Bond Length, Bond Angle, and Bond Enthalpy, Bond Order, Resonance.
- Polarity of Bonds Dipole Moment-Fajan Rules. Kossel - Lewis Approach to Chemical Bonding.
- Lewis Representation of Simple Molecules, Formal Charges, Limitations of Octet Rule.
- Predicting the Geometry of Simple Molecules. Hybridisation- Different Types of Hybridization Involving S, P and D Orbitals- Shapes of Simple Covalent Molecules.
- Formation of Molecular Orbitals, Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (Lcao). Conditions for Combination of Atomic Orbitals - Energy Level Diagrams for Molecular Orbitals.
- Bonding in Some Homo Nuclear Diatomic Molecules- H2, HE2, LI2, B2, C2, N2 and O2. Hydrogen Bonding-Cause of Formation of Hydrogen Bond.
- Types of Hydrogen Bonds-Inter and Intra Molecular- General Properties of Hydrogen Bonds.
- Coordinate Bond - Definition With Examples.
States Of Matter: Gases And Liquids:
- The Gas Laws. Ideal Gas Equation.
- Thermal Energy. Intermolecular Forces vs Thermal Interactions.
- Intermolecular Forces. Graham’s Law of Diffusion - Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures. Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases.
- Behaviour of Real Gases - Deviation From Ideal Gas Behaviour - Compressibility Factor vs Pressure Diagrams of Real Gases.
- Kinetic Gas Equation of an Ideal Gas (No Derivation) Deduction of Gas Laws From Kinetic Gas Equation.
Stoichiometry:
- Laws of Chemical Combinations - Law of Conservation of Mass, Law of Definite Proportions.
- Law of Multiple Proportions, Atomic and Molecular Masses. Mole Concept and Molar Mass.
- Oxidation Number Concept. Percentage Composition of Compounds and Calculations of Empirical and Molecular Formulae of Compounds.
- Stoichiometry and Stoichiometric Calculations-Limiting Reagent.
- Concept of Equivalent Weight. Types of Redox Reactions- Combination, Decomposition, Displacement and Disproportionation Reactions.
- Balancing of Redox Reactions - Oxidation Number. Methods of Expressing Concentrations of Solutions Mass Percent.
- Mole Fraction, Molarity, Molality and Normality. Oxidation and Reduction Reactions.
- Redox Reactions in Terms of Electron Transfer.
Thermodynamics:
- Thermodynamic Terms. The System and the Surroundings. The State of the System. The Internal Energy as a State Function. Types of Systems and Surroundings. (A) Work (B) Heat (C) the General Case, the First Law of Thermodynamics. Extensive and Intensive Properties.
- Absolute Entropy and the Third Law of Thermodynamics. The Relationship Between Cp and CV.
- Measurement of ∆U and ∆H: Calorimetry. Enthalpy Change, ∆Rh of Reactions - Reaction Enthalpy (A) Standard Enthalpy of Reactions, (B) Enthalpy Changes During Transformations, (C) Standard Enthalpy of Formation, (D) Thermo Chemical Equations (E) Hess’s Law of Constant Heat Summation.
- Spontaneity. (A) Is Decrease in Enthalpy a Criterion for Spontaneity? (B) Entropy and Spontaneity, the Second Law of Thermodynamics, (C) Gibbs Energy and Spontaneity.
- Enthalpies for Different Types of Reactions. (A) Standard Enthalpy of Combustion (∆CH0), (B) Enthalpy of Atomization (∆AH0 ), Phase Transition, Sublimation and Ionization, (C) Bond Enthalpy (∆BONDH0), (D) Enthalpy of Solution (SOLH0) and Dilution-Lattice Enthalpy. Applications.
- Work. Enthalpy, H- A Useful New State Function.
Chemical Equilibrium And Acids-Bases:
- Relationship Between KP and Kc. Heterogeneous Equilibria.
- Equilibrium in Physical Process. Equilibrium in Chemical Process - Dynamic Equilibrium. Homogeneous Equilibria, Equilibrium Constant in Gaseous Systems.
- Law of Chemical Equilibrium - Law of Mass Action and Equilibrium Constant. Relationship Between Equilibrium Constant K, Reaction Quotient Q and Gibbs Energy G.
- Factors Affecting Equilibria. Applications of Equilibrium Constant.
- Ionic Equilibrium in Solutions. Arrhenius, Bronsted-Lowry and Lewis Concepts of Acids and Bases.
- Ionisation of Acids and Bases. olubility Product Constant Common Ion Effect on Solubility of Ionic Salts.
- Ionisation of Weak Bases. Common Ion Effect in the Ionization of Acids and Bases- Buffer Solutions. Ionisation Constant of Water and Its Ionic Product- PH Scale-Ionisation Constants of Weak Acids.
- Solubility Equilibria of Sparingly Soluble Salts.
Hydrogen And Its Compounds:
- Heavy Water. Hydrogen as a Fuel.
- Position of Hydrogen in the Periodic Table. Water: Physical Properties. Structure of Water, Ice. Chemical Properties of Water.
- Dihydrogen- Occurrence and Isotopes. Hydrides: Ionic, Covalent, and Non-stoichiometric Hydrides.
- Hard and Soft Water. The Temporary and Permanent Water Hardness.
The S - Block Elements (Alkali And Alkaline Earth Metals):
- Group 1 Elements : Alkali Metals. Atomic and Ionic Radii. The Ionization Enthalpy. Hydration Enthalpy. Physical Properties. The Anomalous Properties of Lithium: Differences and Similarities With The Other Alkali Metals, Diagonal Relationship. Chemical Properties. Uses. The general Characteristics of the Compounds of the Alkali Metals: Oxides. Halides. The salts of Oxo Acids. The Similarities Between Lithium and Magnesium. Some Important Compounds of Sodium: Sodium Chloride
- Group 2 Elements: Alkaline Earth Elements. The Ionization Enthalpy. Some of the Important Compounds of Calcium: Preparation and Uses of Calcium Hydroxide, Plaster of Paris. Cement. The Physical Properties, Chemical Properties. The Oxides, Hydroxides, Halides, Salts of Oxoacids (Carbonates. Sulphates and Nitrates). The General Characteristics of Compounds of the Alkaline Earth Metals: The Anomalous Behaviour of Beryllium. The Diagonal Relationship With Aluminium.
p- Block Elements Group 13 (Boron Family):
- The Important Trends and Anomalous Properties of Boron.
- Uses of Boron, Aluminium and Their Compounds.The General Introduction. The Electronic Configuration. The Atomic Radii, Ionization Enthalpy, Electro Negativity.
- The Physical & Chemical Properties (Note: Aluminum Reactivity Towards Acids & Alkalies Is Deleted).
p-Block Elements - Group 14 (Carbon Family):
- Allotropes of carbon. The Uses of Carbon.
- The General Introduction of Electronic Configuration, Atomic Radii, Ionization Enthalpies, Electro Negativity.
- Any Physical & Chemical Property. The Important Anomalous Properties of Carbon.
Environmental Chemistry:
- Green Chemistry: Green Chemistry in Day-Today Life, The Dry Cleaning of Clothes, The Bleaching of Paper, The Synthesis of Chemicals.
- Definition of Terms: Air, Water and Soil Pollutions, Environmental Pollution. The Atmospheric Pollution, Tropospheric Pollution, Gaseous Air Pollutants (Oxides of Sulphur Oxides of Nitrogen. Hydrocarbons. The Oxides of Carbon (Co, CO2).
- Water Pollution: Causes of Water Pollution. The International Standards for Drinking Water. Global Warming
- Green House Effect, Acid Rain- Particulate Pollutants- Smog.
- The Stratospheric Pollution: Formation and Breakdown of Ozone- Ozone Hole-effects of Depletion of the Ozone Layer.
- Soil Pollution: Pesticides, Industrial Wastes. The Strategies to Control Environmental Pollution.
- Waste Management - Collection and Disposal.
Organic Chemistry-Some Basic Principles And Techniques And Hydrocarbons:
- Nucleophiles and Electrophiles. The Electron Movements in Organic Reactions.
- General Introduction. The Classification of Organic Compounds. Electron Displacement Effects in Covalent Bonds: Inductive Effect, Resonance. The Resonance Effect, Electromeric Effect, Hyperconjugation.
- Alkenes- Nomenclature, Structure of Ethene, Isomerism (Structural and Geometrical). The Tetravalency of Carbon: Shapes of Organic Compounds. The Nomenclature of Organic Compounds.
- The Electrophilic Substitution Reaction, Nitration. The Sulphonation, Halogenation, Friedel-Craft’s Alkylation and Acylation.
- The Fundamental Concepts in Organic Reaction Mechanisms. The Fission of Covalent Bond. Hydrocarbons: All Classification of Hydrocarbons.
- Alkanes - Nomenclature, Isomerism (Structural and Conformations of Ethane Only). The Preparation of Alkanes.
- Properties - Physical Properties and Chemical Reactivity, Substitution Reactions – The Halogenation (Free Radical Mechanism Is Deleted), Controlled Oxidation, Isomerisation, The Aromatization and Reaction With Steam.
- The Directive Influence of Functional Groups in Mono Substituted Benzene. The Carcinogenicity and Toxicity. All Methods of Preparation.
- The Oxidation, Ozonolysis and Polymerization. Alkynes - Nomenclature and Isomerism, the Structure of Acetylene. The Methods of Preparation of Acetylene. Physical Properties and Chemical Reactions. The Acidic Character of Acetylene, Addition Reactions- Of Hydrogen. Halogen, Hydrogen Halides and Water.
- Polymerization. The Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Nomenclature and Isomerism, Structure of Benzene. The Preparation of Benzene. Structural Representations of Organic Compounds.
- All Types of Organic Reactions.
- All Properties- Physical and Chemical Reactions: The Addition of Hydrogen, Halogen, Water, Sulphuric Acid, Hydrogen Halides (Mechanism- Ionic and Peroxide Effect, Markovnikov’s, Anti-markovnikov’s or Kharasch Effect).
Hydrocarbons:
- The Structure of Benzene, Resonance and Aromaticity, The Preparation of Benzene. Oxidation, Ozonolysis and Polymerization, Alkynes - Nomenclature and Isomerism, the Structure of Acetylene. The Classification of Hydrocarbons, Alkanes - Nomenclature, Isomerism (Structural and Conformations of Ethane Only).
- The Preparation of Alkanes. Electrophilic Substitution Reactions- Nitration, Sulphonation, Halogenation. The Friedel-Craft’ Alkylation and Acylation. Any Physical Properties and Chemical Reactivity, Substitution.
- Alkenes- The Nomenclature, Structure of Ethene, Isomerism (Structural and Geometrical). The Physical and Chemical Properties: Mechanism of Electrophilic Substitution. The Directive Influence of Functional Groups in Mono Substituted Benzene, Carcinogenicity and Toxicity.
- Methods of Preparation: The Properties. All Physical and Chemical Reactions: Addition of Hydrogen. Halogen, Sulphuric Acid, Hydrogen Halides (The Mechanism- Ionic and Peroxide Effect, Markovnikov’s, Antimarkovnikov’s or Kharasch Effect).
- Reactions - Halogenation (Free Radical Mechanism), Controlled Oxidation, Isomerisation, Reaction With Steam and Pyrolysis.
- All Methods of Preparation of Acetylene. All Physical Properties and Chemical Reactions. The Acidic Character of Acetylene, Addition Reactions- Of Hydrogen, Halogen, and Water.
- The Polymerization, Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Nomenclature and Isomerism.
Solid State:
- The General Characteristics of Solid State. Bravais Lattices Primitive and Centred Unit Cells. The Amorphous and Crystalline Solids. The Probing the Structure of Solids: X-Ray Crystallography.
- Any Imperfections in Solids. All Crystal Lattices and Unit Cells. The Classification of Crystalline Solids Based on Different Binding Forces (Molecular, Ionic, Metallic and Covalent Solids).
- The Number of Atoms in a Unit Cell (Primitive, Body Centred and Face Centred Cubic Unit Cell). Formula of a Compound and Number of Voids Filled. Tetrahedral and Octahedral Voids.
- The Locating Tetrahedral and Octahedral Voids. The Packing Efficiency in Simple Cubic, BCC and in HCP, CCP Lattice.
- The Close Packed Structures: Close Packing In One Dimension, in Two and Three Dimensions.
- The Calculations Involving Unit Cell Dimensions. All Types of Point Defects-Stoichiometric and Non-stoichiometric.
Solutions:
- Types of Solutions. The Expressing Concentration of Solutions - Mass Percentage, Volume Percentage.
- The Ideal and Nonideal Solutions. Mass by Volume Percentage, Parts per Million. The Mole Fraction, Molarity and Molality.
- The Osmosis and Osmotic Pressure- Reverse Osmosis and Water Purification. The Vapour Pressure of Liquid Solutions: Vapour Pressure of Liquid. Liquid Solutions.
- The Solubility: Solubility of a Solid in a Liquid, Solubility of a Gas in a Liquid. Henry’s Law. The Elevation of Boiling Point-Depression of Freezing Point.
- Law of Raoult as a Special Case of Henry’s Law. The Vapour Pressure of Solutions of Solids in Liquids. The Colligative Properties and Determination of Molar Mass.
- The Relative Lowering of Vapour Pressure.
Electrochemistry And Chemical Kinetics Electrochemistry:
- All Strong Electrolytes and Weak Electrolytes. The Applications of Kohlrausch’s Law.
- The Zero Order Reactions. The Temperature Dependence of the Rate of a Reaction.
- The Half-Life of a Reaction. Conductance of Electrolytic Solutions- The Measurement of the Conductivity of Ionic Solutions.
- The Effect of Catalyst. Electrolytic Cells and Electrolysis: Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis. Electrochemistry: Electrochemical Cells.
- The Equilibrium Constant From Nernst Equation. Factors Influencing the Rate of a Reaction: Dependence of Rate on Concentration.
- The Order of a Reaction, Molecularity of a Reaction. Electrochemical Cell and Gibbs Energy of the Cell Reaction. Nernst Equation.
- The Integrated Rate Equations. Galvanic Cells: Measurement of Electrode Potentials.Variation of Conductivity and Molar Conductivity With Concentration.
- The Products of Electrolysis. Hydrogen Economy.
- The Chemical Kinetics: Rate of a Chemical Reaction. Rate Expression and Rate Constant. Pseudo First Order Reactions.
Chemical Kinetics:
- The Order of a Reaction, Molecularity of a Reaction, Integrated Rate Equations. Zero Order Reactions.
- First Order Reactions- Half Life of a Reaction.
- The Pseudo First Order Reaction. Rate of all Chemical Reactions. The Effect of Catalyst, Collision Theory of Chemical Reaction Rates.
- The Factors Influencing Rate of a Reaction: Dependence of Rate on Concentration, Rate Expression and Rate Constant.
- The Temperature Dependence of the Rate of a Reaction.
Surface Chemistry:
- Adsorption: The Distinction Between Adsorption and Absorption Mechanism of Adsorption.
- The Classification of Colloids: Classification Based on Physical State of Dispersed Phase and Dispersion Medium.
- The Charge on Colloidal Particles, Electrophoresis. Coagulation of Lyophilic Sols and Protection of Colloids. Types of Adsorption.
- The Characteristics of Physisorption. Coagulation.
- The Precipitation Methods. Characteristics of Chemisorption.
- The Adsorption Cleansing Action of Soaps. Multi Molecular, Macromolecular and Associated Colloids. Purification of Colloidal Solutions-Properties of Colloidal Solutions: Colligative Properties, Tyndal Effect, Colour, Brownian Movement.
- The Preparation of Colloids. Isotherms. Colloids.
- The Classification Based on Type of Particles of the Dispersed Phase.
- The Adsorption From Solution Phase. Applications of Adsorption. The Classification Based on Nature of the Interaction Between Dispersed Phase and Dispersion Medium. The Application of Colloids.
General Principles of Metallurgy:
- Occurrence of Metals, The Concentration of Ores-Levigation.
- Froth Flotation, Leaching, The Magnetic Separation.
- The Ellingham Diagram-Limitations, The Application Extraction of Iron, Copper and Zinc From Their Oxides. Extraction of Crude Metal From Concentrated Ore.
- The Conversion to Oxide, Reduction of Oxide to the Metal.
- The Thermodynamic Principles of Metallurgy. Oxidation and Reduction.
- The Refining of Crude Metal-Distillation, Liquation Polling, Electrolytic Refining.
- The Uses of Aluminum, Copper, Zinc and Iron. The Electrochemical Principles of Metallurgy. The Zone Refining and Vapor Phase Refining.
p-Block Elements:
- All Group-15 Elements: Occurrence- Electronic Configuration, Atomic and Ionic Radii, Electronegativity, Preparation and Properties of Nitric Acid. The Physical and Chemical Properties. The Compounds of Nitrogen-Preparation, Properties and Uses of Ammonia. Oxides of Nitrogen (Note: Only Structures Are Deleted). The Dinitrogen-Preparation, Properties and Uses.
- All Group-16 Elements: Sulphuric Acid- Properties and Uses. The Occurrence- Electronic Configuration. Electron Gain Enthalpy, Electronegativity. All Physical and Chemical Properties. The Simple Oxides. The Sulphur Dioxide-Preparation, Properties and Uses. The Ozone-Preparation, Properties, Structure and Uses. Sulphur-Allotropic Forms. Oxoacids of Sulphur.
- Group-17 Elements: Interhalogen Compounds. The Preparation, Properties and Uses. The Chlorinepreparation, Properties and Uses. The Occurrence, Electronic Configuration, Ionisation Enthalpy. The Electron Gain Enthalpy, Electro Negativity, Physical and Chemical Properties. Hydrogen Chloride- The Preparation, Properties and Uses. Oxoacids of Halogens.
- Group-18 Elements: Occurrence, Electronic Configuration, Ionization Enthalpy, Atomic Radii. Electron Gain Enthalpy, All Physical and Chemical Properties (a) Xenon-Fluorine COMPOUNDSXEF2,XEF4 and XEF6 - Preparation, Hydrolysis and Formation of Fluoro Anions-Structures of XEF2, XEF4 and XEF6 (B) Xenon- Oxygen Compounds XEO3 and XEOF4 - Formation and Structures
d and f Block Elements and Coordination Compound
- All The d and f Block Elements: Position in the Periodic Table.
- All General Properties of the Transition Elements (D-Block)
- The Physical Properties, Variation in Atomic and Ionic Sizes of Transition Series. Electronic Configuration of the D-Block Elements. Ionisation Enthalpies, Oxidation States, Trends in the M²+/M and M³+/M²+ Standard Electrode Potentials.
- The Magnetic Properties, Formation of Coloured Ions. Formation of Complex Compounds, Catalytic Properties.
- The Trends in Stability of Higher Oxidation States, Chemical Reactivity and E θ Values. Alloy Formation. Atomic and Ionic Size Oxidation States.
- The Electronic Configuration. Coordination Compounds: Werner’s Theory of Coordination Compounds.
- All Definitions of Some Terms Used in Coordination Compounds. Some Applications of d and f Block Elements.
- All Applications of Coordination Compounds.
- The Nomenclature of Coordination Compounds-Iupac Nomenclature. Bonding in Coordination Compounds. (A) Valence Bond Theory - Magnetic Properties of Coordination Compound Limitations of Valence Bond Theory (B) Crystal Field Theory (I) Crystal Field Splitting in Octahedral and Tetrahedral Coordination Entities (II) Colour in Coordination Compounds.
- The Limitations of Crystal Field Theory.
- The Stability of Coordination Compounds.
Coordination Compounds:
- Werner’s Theory of Coordination Compounds, Nomenclature of Coordination Compounds.
- Definitions of Some Terms Used in Coordination Compounds.
- The Iupac Nomenclature, Isomerism in Coordination Compounds- (A) Stereo Isomerism-Geometrical and Optical Isomerism (B) Structural Isomerism-Linkage, Coordination, Ionisation and Hydrate Isomerism Bonding in Coordination Compounds. (A) Valence Bond Theory - Magnetic Properties of Coordination Compounds-Limitations of Valence Bond Theory (B) Crystal Field Theory (I) Crystal Field Splitting in Octahedral and Tetrahedral Coordination Entities (II) Colour in Coordination Compounds
- The Stability of Coordination Compounds. The Bonding in Metal Carbonyls.
- The Importance and Applications of Coordination Compounds.
Polymers:
- Classification of Polymers.
- The Addition Polymerization or Chain Growth Polymerization.
- The classification Based on Source, Structure, Mode of Polymerization.
- The Molecular Forces and Growth Polymerization.
- All Types of Polymerization Reactions. Teflon and Polyacrylonitrile. Polyamides-Preparation of Nylon 6,6 and Nylon 6.
- The Poly Esters Terylene - Bakelite, Melamine. The Formaldehyde Polymers Copolymerization.
- The Glyptal and Bakelite - Their Monomers, Structures and Uses. Vulcanisation of Rubber. All Synthetic Rubbers.
- The Molecular Mass of Polymers-Number Average and Weight Average Molecular Masses.
- The Poly Dispersity Index (PDI). Biodegradable Polymers. Phbv, Nylon 2-Nylon 6. Polymers of Commercial Importance Polypropene, Polystyrene, Polyvinylchloride (PVC).
Biomolecules:
- Carbohydrates - Classification of Carbohydrates- Monosaccharides: Preparation of Glucose From Sucrose and Starch.
- The Properties and Structure of Glucose - D, L Configurations and (+), (-) Configurations of Glucose.
- The Structure of Fructose Invert Sugar. The Structures of Maltose and Lactose. Polysaccharides: Structures of Starch, Cellulose and Glycogen.
- All Classification of Amino Acids - Structures and D and L Forms.
- The Importance of Carbohydrates (Note: Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose, Starch, Carbohydrates Importance Is Deleted).
- The Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary Structures of Proteins.
- The Disaccharides: Sucrose- Preparation, Structure. Proteins: Aminoacids: Natural Aminoacids. Zwitter Ions.
- The Proteinsstructures, Classification, Fibrous and Globular.
- The Denaturation of Proteins. Vitamins: Explanation. Names.
- The Classification of Vitamins. Deficiency Diseases of Different Types of Vitamins.
- The Sources of Vitamins. Nucleic Acids: Chemical Composition of Nucleic Acids.
- The Structures of Nucleic Acids, Biological Functions of Nucleic Acids.
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes:
- Classification and Nomenclature.
- The Methods of Preparation: Alkyl Halides and Aryl Halides- From Alcohols, From Hydrocarbons (A) by Free Radical Halogenation (B) by Electrophilic Substitution (C) by Replacement of Diazonium Group (Sandmeyer Reaction) (D) by the Addition of Hydrogen Halides and Halogens to Alkenes-by Halogen Exchange Reactions.
- The Reactions of Haloarenes: (I) Nucleophilic Substitution (II) Electrophilic Substitution and (III) Reaction With Metals.
- The Nature of C-X Bond.
- All Chemical Reactions: Reactions of Haloalkanes (I) Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions (A) Sn² Mechanism (B)Sn¹ Mechanism (C) Stereochemical Aspects of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions- Optical Activity (II) Elimination Reactions (III) Reaction With Metals.
- All Physical Properties-Melting and Boiling Points, Density and Solubility.
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers:
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - Classification
- Nomenclature of (A) Alcohols, (B) Phenols and (C) Ethers Structures of Hydroxy and Ether Functional Groups.
- All Methods of Preparation: Alcohols From Alkenes and Carbonyl Compounds
- The From Grignard Reagents. Phenols From Haloarenes, Benzene Sulphonic Acid, Diazonium Salts, Cumene Physical Properties of Alcohols and Phenols.
- The Tiemann Reaction, Reaction With Zinc Dust, Oxidation, Commercially Important Alcohols (Methanol, Ethanol).
- The Chemical Reactions of Alcohols and Phenols (i) Reactions Involving Cleavage of O-H Bond in Alcohols-Acidity of Alcohols and Phenols, Esterification (ii) Reactions Involving Cleavage of C-O Bond- Reactions With Hx, PX3 , Dehydration and Oxidation (iii) Reactions of Phenols- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution, Kolbe’s Reaction, Reimer. Ether.
- All Methods of Preparation: By Dehydration of Alcohols.
- The Chemical Reactions: Cleavage of C-O Bond and Electrophilic Substitution of Aromatic Ethers (Anisole). Williamson Synthesis. Physical Properties.
Aldehydes and Ketones:
- The Nomenclature and Structure of Carbonyl Group.
- All Uses of Aldehydes and Ketones.
- The Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones-(1) by Oxidation of Alcohols (2) by Dehydrogenation of Alcohols (3) From Hydrocarbons.
- The Preparation of Aldehydes (1) From Acyl Chlorides (2) From Nitriles and Esters (3) From Hydrocarbonspreparation of Ketones
- (1) From Acyl Chlorides (2)From Nitriles (3) From Benzene or Substituted Benzenes.
- The Chemical Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones.
- The Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones.
- The Nucleophilic Addition, Reduction, Reactions Due to Hydrogen and Other Reactions (Cannizzaro Reaction, Electrophilic Substitution Reaction), Oxidation.
Carboxylic Acids:
- All Nomenclature and Structure of Carboxyl Group.
- All the Methods of Preparation of Carboxylic Acids (1) From Primary Alcohols and Aldehydes (2) From Alkyl Benzenes (3 )From Nitriles and Amides (4) From Grignard Reagents (5) From Acyl Halides and Anhydrides (6) From Esters.
- All the Chemical Reactions: (i) Reactions Involving Cleavage of O-H Bond-Acidity, Reactions With Metals and Alkalies (ii) Reactions Involving Cleavage of C-Oh Bond-Formation of Anhydride, Reactions With PCL5 , PCL3, SOCL2, Esterification and Reaction With Ammonia (iii) Reactions Involving-Cooh Group-Reduction, Decarboxylation (iv) Substitution Reactions in the Hydrocarbon Part
- The Halogenation and Ring Substitution. Any and All Physical Properties.
- All The Uses of Carboxylic Acids.
Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen:
- Amines: Structure of Amines. Nomenclature.
- The Preparation of Amines: Reduction of Nitro Compounds, Ammonolysis of Alkyl Halides, Reduction of Nitriles.
- Reduction of Amides, Gabriel Phthalimide Synthesis and Hoffmann Bromamide Degradation Reaction.
- All Physical Properties.
- All the Chemical Reactions: Basic Character of Amines, Alkylation, Acylation, Carbyl Amine Reaction.
- Reaction With Nitrous Acid, Reaction With Aryl Sulphonyl Chloride
- The Electrophilic Substitution of Aromatic Amines (Aniline) - Bromination, Nitration and Sulphonation.
- Cyanides and Isocyanides: Structure and Nomenclature of Cyanides and Isocyanides. Chemical Reactions of Cyanides and Isocyanide.
- All The Physical Properties. Preparation.
Don't Miss: How to Crack AP EAMCET 2025?
Chemistry AP EAMCET Weightage 2025
The Chemistry weightage for AP EAMCET 2025 emphasises the critical topics within the syllabus. These topics are identified for being asked frequently in the AP EAMCET question paper. Focusing on high-weightage topics will ensure that a major chunk of the syllabus is covered for the exam.
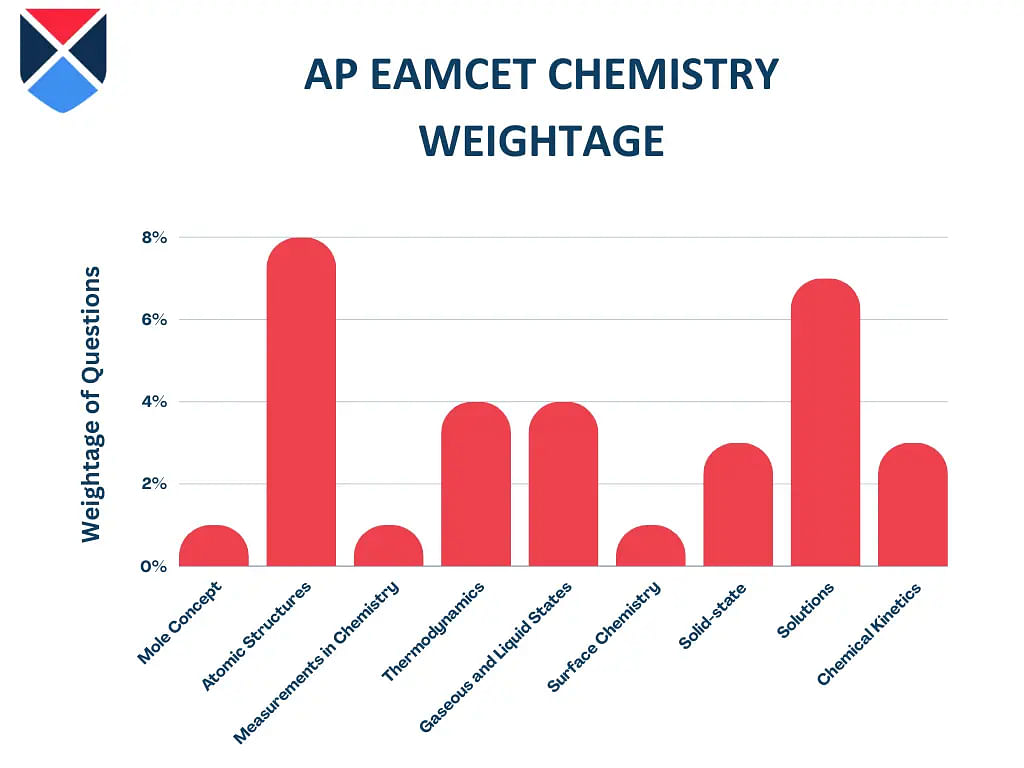
In the following table, AP EAMCET chemistry chapter wise weightage is highlighted for reference:
| Topics | Weightage (Approx) |
| Mole Concept | 1% |
| Atomic Structures and Chemical Bonding | 8% |
| Measurements in Chemistry | 1% |
| Thermodynamics | 4% |
| Gaseous and Liquid States | 4% |
| Surface Chemistry | 1% |
| Solid-state | 3% |
| Solutions | 7% |
| Chemical Kinetics | 3% |
Also Attempt: AP EAMCET Mock Test 2025
AP EAMCET 2025 Chemistry Syllabus: Reference Books
For all-round preparation, candidates must utilise as many AP EAMCET reference books 2025 as possible. Students must ensure that the reference books provide foundational overview and in-depth topics for the AP EAMCET 2025 Chemistry syllabus. Students can avail the following books online or offline for sale:
- “EAMCET” Chemistry by Arihant Publications
- “Class 11 and 12 Chemistry Textbook” by NCERT
- “Concise Inorganic Chemistry” by J.D. Lee
- “Physical Chemistry” by P. Bahadur
- “Organic Chemistry” by O. P. Tandon
Also Read: AP EAMCET Qualifying Marks 2025
AP EAMCET Chemistry 2025 Syllabus Preparation Tips
A variety of tactics can be included in a student’s study plan to study the Chemistry AP EAMCET Chemistry question 2025. Students muct inculcate the following recommendations to boost the exam preparation strategies:
- Understand the in-depth topics of AP EAMCET Chemistry syllabus 2025.
- Work on reinforcing high-weight topics to cover the major parts of the syllabus.
- Solving the AP EAMCET previous year papers will familiarise students with the question format and frequently appearing questions.
- Candidates must allot a lot of time to studying Chemical reactions and equations. These are an integral part of the AP EAMCET Chemistry syllabus 2025.
- Utilising video tutorials to focus on Chemistry topics can help in understanding the functionalities of various equations, elements, etc. When students learn through visual aid, the equations are ingrained properly. YouTube, Unacademy, and Khan Academy host in-depth video lectures and tutorials for AP EAMCET syllabus 2025 Chemistry.
- Students may use flashcards, or have a separate notebook to write down important terminology and periodic element names.
- Reviewing different study material such as NCERT textbooks, subject-specific journals, well-researched papers, and relevant articles to understand any upcoming trends in the field.
- To enhance their revision, students can solve the AP EAMCET mock tests and previous year papers. Solving these question papers will also boost the students’ speed when attempting the exam.
- Students must rest by taking regular interval breaks between the study sessions. This will rejuvenate the student’s mind and keep them motivated.
Recommened: AP EAMCET Books 2025