Table of Contents
-
WBJEE Chemistry Syllabus 2025 will soon be made available for download in a PDF format by the WBJEEB. The WBJEE 2025 Chemistry syllabus contains topics such as Atomic Structure, Coordination Compounds, States of Matter, Chemical Dynamics, Alcohol, etc.
The WBJEE Syllabus 2025 for Chemistry is based on the topics covered in the Class XI and XII syllabus. The topics and chapter-wise weightage of the WBJEE Chemistry syllabus are discussed in detail on this page. Students must refer to the Chemistry important topics, and chapter-wise weightage of the WBJEE Exam to prepare well for the exam.
WBJEE Chemistry Syllabus 2025 PDF
Students appearing for the WBJEE exams can access the WBJEE Chemistry syllabus 2025 PDF from the link given below. The WBJEE 2025 Chemistry Syllabus PDF contains all the important topics and sub-topics that students must cover for the exam.
| WBJEE Chemistry Syllabus PDF 2025 | Download PDF |
Practice Now: WBJEE Previous Year Question with Solution
Topic-wise WBJEE Chemistry Syllabus 2025
The WBJEE Chemistry Syllabus 2025 is discussed in detail below. Students are advised not to skip any topics for better results.
Atoms, Molecules and Chemical Arithmetic
- Dalton’s Atomic Theory.
- Gay Lussac’s Law of Gaseous Volume.
- Avogadro’s Hypothesis and Applications.
- Atomic Mass, Molecular Mass, Equivalent Weight.
- Mole Concept, Gram Atomic Weight, Molecular Weight.
- Gramequivalent Weight and Mole Concept.
- Chemical Formulae and Balanced Chemical Equations.
- Calculations Involving Oxidation–Reduction, Neutralization, and Displacement Reactions.
- Concentration Terms: Mole Fraction, Molarity, Molality, and Normality.
- Percentage Composition, Empirical Formula, Molecular Formula.
- Numerical Problems.
Atomic Structure:
- Concept of Nuclear Atom.
- Electron, Proton, and Neutron Properties.
- Atomic Number, Rutherford’s Model, and Limitations.
- Line Spectra of Hydrogen Atom.
- Quantization of Energy (Planck’s Equation E = Hν).
- Bohr’s Model, Sommerfeld’s Modifications.
- Quantum Numbers, Electronic Configurations.
- Aufbau Principle, Pauli’s Exclusion Principle, Hund’s Rule.
- Dual Nature of Matter & Light, de Broglie’s Relationship.
- Atomic Orbitals, Shapes of S, P, & D Orbitals.
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Chemistry
Radioactivity and Properties of α-, β-, γ Rays.
- Artificial Transmutation.
- Rate of Radioactive Decay, Decay Constant, Half-Life.
- Radioisotopes and Their Uses (C, P, Co, I).
- Isobars and Isotones, Nuclear Fission & Fusion Reactions.
- Group Displacement Law, Stability of Atomic Nucleus.
The Periodic Table and Chemical Families
- Modern Periodic Law.
- Periodic Table Based on Electronic Configurations.
- Groups (GR. 1-18) and Periods.
- Representative (S-Block and P-Block), Transition (D-Block), Inner Transition (F-Block) Elements.
- Periodic Trends in Physical and Chemical Properties.
- Position of Hydrogen and Noble Gases.
- Diagonal Relationships.
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Valence Electrons, Octet Rule, Electrovalent, Covalent, and Coordinate Covalent Bonds.
- Limitations of Octet Rule, Fajans Rule.
- Directionality of Covalent Bonds, Shapes of Poly-Atomic Molecules.
- Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals (SP, SP2, SP3, & DSP2).
- Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram for Homonuclear Diatomic Species.
- Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (Vsepr) Concept.
- Concept of Resonance, Electronegativity, Bond Polarity, Dipole Moment.
- Hydrogen Bonding & Its Effects on Physical Properties.
- Hydrogen Bridge Bonds in Diborane.
Coordination Compounds
- Introduction, Double Salts, and Complex Salts.
- Coordination Compounds (Examples Only).
- Werner’s Theory, Coordination Number, Colour, Magnetic Properties, Shapes.
- IUPAC Nomenclature of the Mononuclear Coordination Compounds.
Solid State
- The Classification of Solids Based on the Different Binding Forces.
- Molecular, Ionic, Covalent, & Metallic Solids.
- Amorphous & Crystalline Solids.
- Unit Cell, Density of Unit Cell, Packing in Solids, Packing Efficiency.
- Voids, No. Of Atoms per Unit Cell, Point Defects.
- Electrical & Magnetic Properties, the Band Theory of Metals.
- Conductors, Semiconductors, Insulators, N & P Type Semiconductors.
Liquid State
- Vapour Pressure, Viscosity, & Surface Tension (Qualitative Idea).
Gaseous State
- Measurable Properties of Gases.
- Boyle’s Law, Charles Law, Absolute Scale of Temperature.
- Kinetic Theory of Gases, Ideal Gas Equation.
- Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure, Grahams Law.
- Deviations From Ideal Behavior, the Liquefaction of Gases.
- The Real Gases, Van Der Waals Equation, Numerical Problems.
Chemical Energetics and Chemical Dynamics
- Conservation of Energy Principle.
- Energy Changes in Physical and Chemical Transformations.
- First Law of Thermodynamics, Internal Energy, Enthalpy.
- Hess’s Law and Its Applications (Numerical Problems).
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics, Entropy, Free Energy, Criterion of Spontaneity.
- Third Law of Thermodynamics (Brief Introduction).
- Law of Mass Action, the Dynamic Nature of Chemical Equilibria.
- Equilibrium Constants, the Le Chatelier’s Principle.
- Equilibrium Constants of Gaseous Reactions (KP & Kc) and Relation Between Them.
- Significance of δG and δGº, Factors Affecting the Rate of Chemical Reactions.
- Concept of Collision Theory, Arrhenius Equation, Activation Energy.
- Order and Molecularity, First Order Reactions, Rate Constant, Half-Life (Numerical Problems).
Physical Chemistry of Solutions
- Colloidal Solutions, Differences From True Solutions.
- Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Colloids, Coagulation, Peptization.
- Dialysis & Its Applications, Brownian Motion, Tyndall Effect.
- Emulsion – Types of Emulsions, Electrolytic Solutions.
- Specific Conductance, the Equivalent Conductance, Ionic Conductance.
- Kohlrausch’s Law, the Faraday’s Laws of Electrolysis, Application, Numerical Problems.
- The Non-electrolytic Solutions, Types of Solution, Vapour Pressure of Solutions.
- The Raoult’s Law, Colligative Properties, Osmotic Pressure.
- Relationships With Molecular Mass , Numerical Problems.
Ionic & Redox Equilibria
- Ionic Equilibria, the Ionization of Weak Electrolytes.
- Ostwald’s Dilution Law, the Ionization Constants of Weak Acids and Bases.
- Ionic Product of Water, PH Scale, PH of Aqueous Solutions.
- Buffer Solutions, Henderson Equation.
- Acid-Base Titrations, Acid-Base Indicators.
- Hydrolysis of Salts (Elementary Idea), the Solubility Product.
- Common Ion Effect, Redox Equilibria.
- Oxidation–Reduction Reactions, Electron Transfer Processes.
- Oxidation Numbers, Balancing of Redox Reactions.
- Standard Electrode Potentials (E°), Electrochemical Series.
- Feasibility of a Redox Reaction, Significance of Gibbs Equation.
- Redox Titrations With Examples, Nernst Equation (Numerical Problems).
Hydrogen
- The Position of Hydrogen in the Periodic Table, Occurrence, Isotopes.
- Preparation, Properties, and Uses of Hydrogen.
- Hydrides - Ionic, Covalent, & Interstitial.
- Physical & Chemical Properties of Water, Heavy Water.
- Hydrogen Peroxide - Preparation, Reactions, Structure, and Use.
- Hydrogen as a Fuel.
Chemistry of Non-metallic Elements and Their Compounds
- Carbon – Occurrence, Isotopes, Allotropes (Graphite, Diamond, Fullerene).
- Co and CO2 Production, Properties, and Uses.
- Nitrogen and Phosphorus – Occurrence, Isotopes, Allotropes.
- Isolation From Natural Sources, Purification, Reactivity of Free Elements.
- The Preparation, Properties, Reactions of NH3, PH3, No, NO2, HNO2, HNO3, p4o10, h3po3, and H3po4.
- Oxygen and Sulphur – Occurrence, Isotopes, Allotropic Forms.
- Isolation From Natural Sources, Purification, Properties & Reactions of the Free Elements.
- Water, the Unusual Properties of Water, Heavy Water (Production and Uses).
- Hydrogen Peroxide & Ozone (Production, Purification, Properties & Uses).
- Halogens – A Comparative Study, Occurrence, the Physical States and Chemical Reactivities of the Free Elements.
- Peculiarities of Fluorine & Iodine; Hydracids of Halogens.
- Preparation, Properties, Reactions and Uses.
- Inter-Halogen Compounds (Examples); Oxyacids of Chlorine.
Chemistry of Metals
- General Principles of Metallurgy
- Occurrence, Concentration of Ores
- Production and Purification of Metals
- Mineral Wealth of India
- Properties and Reactions of Typical Metals (NA, CA, Al, Fe, CU, Zn)
- Manufacture of Steels & Alloy Steel (Bessemer, Open-Hearth, & l.d. Process)
- the Principles of Chemistry Involved in Electroplating, Anodizing, and Galvanizing
- Preparation and Properties of k2cr2o7 and KMNO4
- Lanthanoids – Electronic Configuration, Oxidation States, Chemical Reactivity, Lanthanoid Contraction and Its Consequences
- Actinoids – Electronic Configuration, Oxidation States, Comparison With Lanthanoids
Chemistry in the Industry
- Large Scale Production & Uses of Sulphuric Acid (Contact Process)
- Ammonia (Haber’s Process), Nitric Acid (Ostwald’s Process)
- Sodium Bicarbonate and Sodium Carbonate (Solvay Process)
Polymers
- Natural and Synthetic Polymers
- Methods of Polymerization (Addition and Condensation), Copolymerization
- Some Important Polymers – Natural and Synthetic
- Polythene, Nylon, Polyesters, Bakelite, Rubber
- Biodegradable and Non-biodegradable Polymers
Surface Chemistry
- Adsorption – Physisorption and Chemisorption
- Factors Affecting Adsorption of Gases on Solids
- Catalysis, Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysis, Activity & Selectivity
- The Enzyme Catalysis, Colloidal State, the Distinction Between True Solutions, Colloids, & Suspension
- Lyophilic, Lyophobic, Multimolecular & the Macromolecular Colloids
- The Properties of Colloids, the Tyndall Effect, the Brownian Movement, Electrophoresis, Coagulation, & Emulsion – Types
Environmental Chemistry
- The Common Modes of Pollution of Air, Water, & Soil
- Ozone Layer, Ozone Hole, Chemical Reactions in Atmosphere, Smog
- Major Atmospheric Pollutants, the Green House Effect, Global Warming
- Pollution Due to Industrial Wastes, Green Chemistry an Alternative Tool for Reducing Pollution
- Strategies for Control of Environmental Pollution
Chemistry of Carbon Compound
- Hybridization of Carbon: Σ – And Π – Bonds
- Isomerism – Constitutional and Stereoisomerism
- Geometrical & Optical Isomerism of Compounds Containing Up to 2 Asymmetric Carbon Atoms
- The Iupac Nomenclature of Simple Organic Compounds – Hydrocarbons, Mono, & Bifunctional Molecules Only (Alicyclic & Heterocyclic Compounds Excluded)
- Conformations of Ethane & N-Butane (Newman Projection Only)
- Electronic Effects: Inductive, Resonance, & Hyperconjugation
- Stability of Carbocation, Carbanion, & Free Radicals
- The Rearrangement of Carbocation
- Electrophiles & Nucleophiles, Tautomerism in β-Dicarbonyl Compounds
- Acidity & Basicity of the Simple Organic Compounds
Compounds
- Alkanes – The Preparation From Alkyl Halides and Carboxylic Acids
- Reactions — Halogenation & Combustion
- Alkenes & Alkynes – Preparation From Alcohols
- The Formation of Grignard Reagents & Their Synthetic Applications
- SN1 & SN2 Reactions (Preliminary Concept)
- Markownikoff’s & Anti-markownikoff’s Additions; Hydroboration
- The Oxymercuration-Demercuration, Reduction of Alkenes & Alkynes (H2/Lindler Catalyst & NA in Liquid NH3), the Metal Acetylides
- Haloalkanes & Haloarenes
- Haloalkanes – The Preparation From Alcohols
- Nomenclature, Nature of C -X Bond, the Physical & Chemical Properties
- Mechanism of Substitution Reactions, the Optical Rotation
- The Formation of Grignard Reagents & Their Synthetic Applications
- SN1 & SN2 Reactions (Preliminary Concept)
- Uses & Environmental Effects Of - The Dichloromethane, Trichloromethane, Tetrachloromethane, Iodoform, Freons, and Ddt
Alcohols
- The Preparation of Alcohols From Carbonyl Compounds & Esters
- Reaction – Dehydration, Oxidation, Reaction With Sodium, ZNCL2/Hcl, and Phosphorous Halides
Ethers
- Preparation of Ether by the Williamson’s Synthesis
- Cleavage With Hcl & Hi
Aldehydes & Ketones
- The Preparation From Esters, Acid Chlorides, Gem-Dihalides, Ca-Salt of Carboxylic Acids
- Reaction – Nucleophilic Addition With Hcn, Hydrazine, Hydroxylamines, Alcohols
- The Aldol Condensation, Clemmensen & Wolff – Kishner Reduction, Haloform, Cannizzaro & Wittig Reactions
Carboxylic Acids
- Hydrolysis of Esters (Mechanism Excluded) & Cyanides
- Hunsdicker & Hvz Reactions
Aliphatic Amines
- Preparation From Nitro, Cyano, & Amido Compounds
- Distinction of 1º, 2º, 3º Amines (Hinsberg Method)
- Reaction With HNO2, Carbyl Amine Reaction
Benzene
- Kekule Structure, Aromaticity, and Hückel Rule.
- Electrophilic Substitution Reactions: Halogenation, Sulfonation, Nitration, Friedel-Crafts Reaction, Ozonolysis.
- Directive Influence of Substituents in Monosubstituted Benzenes.
- Carcinogenicity and Toxicity.
Amines
- Preparation From the Reduction of the Nitro Compounds.
- Formation of Diazonium Salts and Stability.
- Replacement of Diazonium Group With the H, Oh, X (Halogen), CN, & NO2.
- Diazocoupling & Reduction.
Haloarenes
- The Nature of C -X Bond, Substitution Reactions.
- Nucleophilic Substitution, the Cine Substitution (Excluding Mechanism).
- Directive Influence of Halogen in the Monosubstituted Compounds Only.
Phenols
- Halogenation, Sulfonation, Nitration, Reimer–Tiemann, & Kolbe Reactions.
Aromatic Aldehydes
- Preparation by the Gattermann, Gattermann-Koch, Rosenmund, and Stephen’s Method.
- Reactions: Perkin, Benzoin, and Cannizzaro.
Application Oriented Chemistry
- Main Ingredients
- Chemical Natures (Structures Excluded)
- Side Effects of Common Antiseptics, Analgesics, Antacids, Vitamin-C.
Introduction to Bio-Molecules
- Carbohydrates: Pentoses and Hexoses. Distinctive Chemical Reactions of Glucose.
- Amino Acids: Glycine, Alanine, Aspartic Acid, Cysteine (Structures). Zwitterion Structures of Amino Acids, Peptide Bond.
- Adp and Atp Structures and Their Role in Bioenergetics.
- Nucleic Acids: Dna and Rna Skeleton Structures. Names of Essential Elements in the Biological System.
Principles of Qualitative Analysis
- Detection of Water-Soluble Non-interfering Acid and Basic Radicals by Dry and Wet Tests.
- Acid Radicals: The CL-, S2-, SO4^2-, NO3–, CO3^2-.
- The Basic Radicals: CU2+, AL3+, FE3+, FE2+, ZN2+, CA2+, MG2+, NA+, NH4+.
- The Detection of Special Elements (N, CL, BR, I, and S) in Organic Compounds by the Chemical Tests.
- The Identification of Functional Groups in Phenols, Aromatic Amines, Aldehydes, Ketones, & Carboxylic Acids.
Don't Miss: How to prepare for WBJEE in 3 months?
Important Topics in the WBJEE Chemistry Syllabus 2025
Students must focus on the important topics from the Chemistry WBJEE Syllabus. The importance of topics depends on the weightage of the topic. Therefore, students should concentrate on the topics and subtopics with a higher weightage to prepare for the exam.
The important topics from the WBJEE Chemistry Syllabus 2025 include:
- Chemical Kinetics.
- Chemical Bonding.
- Hydrocarbons
- Coordination Compounds
- P- Block Elements
- Redox Reactions
- Carboxylic Acids
- Alcohol
- Phenol
- Ether
- Chemical Thermodynamics
- Ionic Equilibrium
- Environmental Chemistry
- Gaseous State
- Solid State
Also Read: How to prepare for WBJEE in 1 Month?
WBJEE Chemistry Weightage 2025
Students must focus on the important topics from the Chemistry WBJEE Syllabus. The important topics are the ones high probability of occurring in the WBJEE Chemistry question paper. Thus, it is advisable to prepare these topics well and revise consistently.
The important topics from the WBJEE Chemistry Syllabus 2025 include the following:
| Important Topics | Chapter Weightage |
| Chemical Kinetics | 7% |
| p- Block Elements | 6% |
| Chemical Bonding | 6% |
| Redox Reactions | 5% |
| Ionic Equilibrium | 4% |
| Chemical Equilibrium | 4% |
| Coordination Compounds | 4% |
| Carboxylic Acids & Derivatives | 4% |
| Alcohol Phenol Ether | 4% |
| Chemical Thermodynamics | 4% |
| Transition Elements (d & f block) | 6% |
| S block elements | 6% |
| Organic Chemistry | 6% |
Also Read: WBJEE Chapter-Wise Weightage 2025
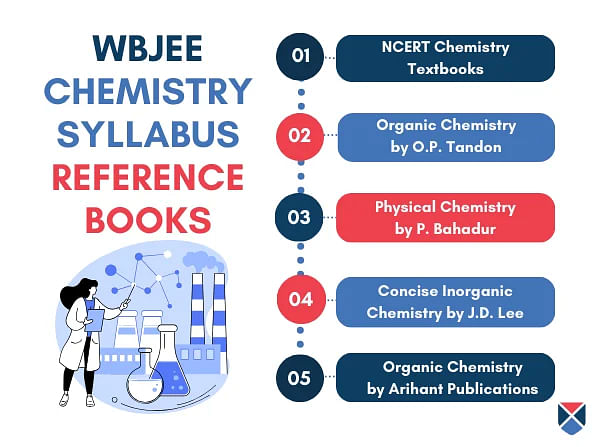
Books for WBJEE Chemistry Preparation
The WBJEE 2025 Chemistry syllabus is based on the Class XI and XII standards curriculum. Therefore, it is important for students to refer to Class XI and XII books.
Students can also refer to additional WBJEE reference books that help in an in-depth understanding of the syllabus. Below is a list of preparation and reference books that students can refer to for WBJEE Chemistry Syllabus preparation:
| Books | Author |
| NCERT Class XI Chemistry | NCERT |
| NCERT Class XII Chemistry | |
| Physical Chemistry | P .Bahadur |
| Organic Chemistry | O.P. Tandon |
| Concise Inorganic Chemistry | J.D. Lee |
| Modern Approaches to Chemical Calculations | R.C. Mukherjee |
| Organic Chemistry | Arihant Publications |
Get the WBJEE Reference Books for all the subjects.
Preparation Tips for WBJEE Chemistry Syllabus 2025
Students are advised to follow strategic and unique preparation methods to improve their chances of passing the exam. Below are some preparation tips that can aid students in their effective preparation:
- Understand the WBJEE exam pattern 2025 and syllabus to not miss any important topics.
- Refer to the WBJEE previous year's question papers and solve them to gauge the structure of the exam and the difficulty level.
- Attempt WBJEE mock test 2025 to stimulate exam conditions and work on time management.
- Use the information on the high-weightage topics provided in the table above and focus on them for better scores.
- Create a realistic study schedule to cover all the topics and sub-topics.
- Note down challenging topics and qfore the exam date, to avoid luestions for a focused revision to strengthen them.
- Start preparing for the exams in advance, preferably 6 months beast-minute stress.
- Use a notebook to note down formulas, definitions, and key concepts that you can refer to at any time.
- For better understanding, make use of online resources like educational websites and YouTube that provide explanations for complex topics.
- Take breaks in between studies to avoid burnout.
Read More: WBJEE Preparation 2025